In our last article “ 5 ways to save tax for sole proprietor” we had seen some basic things how a sole proprietor can save tax and grow his business.
In this article we will see in detail what are other tax saving tools for small business class which will also help him to grow his business along with tax saving.
Till now, we had seen what sole proprietor is and how he is taxed under Income Tax.
Now we will see what are tax planning tools for small business class like sole proprietor.
What is tax planning and tax evasion?
Tax Planning is the term which not only covers various scenarios of tax filing but also focuses on need of reducing tax liability and tax saving. BY way of tax planning one can save tax legally. Tax Evasion is an illegal way of saving tax. Tax evasion is done with motive of showing lesser profits and showing wrong information at the time of filing tax return. Which in future will leads to penalties and interest.
Tax Evasion
How tax planning helps in minimizing taxation?
If one plans his savings and business properly, he can save tax by way of planning which is legal also and as per rules also.
With the help of proper planning one can utilize maximum allowances given by department and minimize his tax liability.
To understand tax planning one need to understand how income is calculated for tax purpose
What is taxable income?
The process of tax planning begins with computation of your Gross Total Income (GTI). For this one need to add all income received by him during the year and club it together to arrive at Gross Total Income and from this GTI one can claim deductions allowed for investments like LIC, PPF, Housing loan and then arrive at taxable income.
Based on tax slab applicable to you, one will calculate tax on taxable income. Now, here comes tax planning part.
Tax planning will include which all expenses are allowed for sole proprietor to claim as deduction from income and then which all investments are allowed as deduction from this total income.
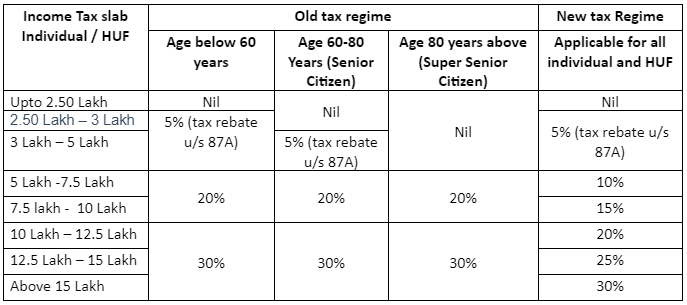
Income tax slab for FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24)
When you know what is your taxable income, next step is to know under which tax slab your income fall.
Every year Government of India notifies tax slabs for all person covered under Income Tax.
Below are tax slabs for individuals
New tax regime analysis
Alternative tax regime what we call as New tax regime was introduced in Budget 2020 which is effective from 1st Apr 2020. AY 2021-22 (FY 2020-21) was the first year when tax returns are filed under new tax regime.
This new tax regime u/s 115BAC gives individual and HUF an option to offer taxation under lower rate at the cost of forgoing some benefits and deductions available under Income Tax.
This is introduced with the intension to reduce taxation of person having income below Rs. 5 Lakh and reduce tax burden of the common and lower income range people.
New tax regime points to remember
- Opting for new tax regime is optional for tax payers
- In this new tax regime, taxpayer has an OPTION to choose either
- To pay tax at lower tax rates as per new regime at the cost to forgo certain permissible exemptions and deductions available under Income Tax, or
- To continue paying taxes as per old regime and enjoy rebate and exemptions, deductions as stated in old tax regime and pay tax at higher rate as per existing tax rates.
- Under new tax regime tax slabs are all same for individuals including NRI below 60 years and above 60 years and super senior citizens above 80years. No increased basic exemptions limit benefit is available based on your age like it is available in old tax regime and this is applicable to NRI as well.
- Tax rebate u/s 87A is available under old and new both regime and net taxable income less than Rs. 5 Lakh will be eligible for tax rebate u/s 87A upto Rs. 12,500/-. Thus person having net taxable income below Rs. 5 Lakh will pay zero tax.
- Additional health and educational cess @4% will be added to income tax liability in all cases
- Surcharge applicable as per tax rates below in all categories mentioned above:
- 10% of Income tax if total income > Rs.50 lakh
- 15% of Income tax if total income > Rs.1 crore
- 25% of Income tax if total income > Rs.2 crore
- 37% of Income tax if total income > Rs.5 crore
- The option to opt for old or new tax regime is available to person every year if you do not have business income. For person having business income, once opt for new regime can not be revoked later on. However salaried employee have option to opt for old or new regime every year
Deductions and Exemptions not available under new tax regime
Any taxpayer opting for new tax regime will have to forgo certain exemptions and deductions which are available under old tax regime. In all 70 deductions and exemptions are not allowed under new tax regime. Some of common used by business class are listed here:
- Interest on housing loan u/s 24
- Additional depreciation for manufacturing units
- Expenditure on scientific Research
- Set off of brought forward losses not allowed under new tax regime for both business loss or unabsorbed depreciation.
- Deductions under chapter VI A (80C, 80D, 80E and so on)( Except section 80CCD(2))
Which Tax Regime is better?
New tax regime is beneficial to taxpayers who are having income upto Rs. 15 Lakh and low investments in the sense which are allowed under income tax under chapter VI A like LIC, Housing Loan, PPF, PF and some other.
Lower investment in tax saving schemes and no business losses in earlier years and under Rs. 15 Lakh income, New tax regime is beneficial.
If you are planning for wealth creation by investment in tax saving schemes like LIC, PPF, PF, mediclaims, old tax regime helps you with higher tax deductions and lower tax outgo.
Higher investments in tax saving schemes, Old tax regime is beneficial.
Tax planning tools for sole proprietor
Investments as Deductions
Advance Tax on TDS
Expenses allowed as deduction from business income
- Depreciation
- Money value of asset decreases over period of time due to usage. Income Tax allows this decreasing money value of any asset used in business as depreciation claim and allowed as business expense
- Thus one should be very much aware about which assets are allowed to claim depreciation and it’s allowed expense
- If you are running manufacturing unit and not using new tax regime, one can claim additional depreciation also to save tax
- Salary to self family members
- If any one from family is assisting you to run business, then it is advisable to pay salary to self family members, as salary is allowed as business expense.
- By doing this, you will save tax in business also and income will also be generated for family member.
- Professional service fees
- If you are taking advise of any professional consultant to run business like accounting services or advocate services or any other service, payment made to these professionals is allowed as business expense
- Travelling and Accommodation
- Any expense incurred on travelling for purpose is allowed as deduction from business income
- Best way to claim this expense is book your travel tickets in business name and claim it as expense in business
- Marketing Expenses
- Any expense incurred on marketing of business like advertisement in paper or online advertisement is allowed as expense.
- Digital marketing will allow business grow speedily and also it can save tax by claiming deduction from income
- Regular business expenses
- One can claim deduction for expenses incurred on printing, repairs, salary, electricity, postage and courier, internet and telephone bills paid for running business.
- Telephone and Internet bills
- Now a days internet is most common expense for business, as without internet one can not run his business as most of transactions are digital now.
- Thus telephone and internet bills are allowed as business expense.
- Interest on business loans
- If any loan is taken from banking or financial institution to run business, then interest paid on such loans is allowed as business expense.
- By way of loan one can save tax also by claiming interest deduction and in other way by keeping self money safe in some other investments earn interest income also on that investments
- Interest on unsecured loans
- If you had taken loan from any relative or family member, then interest paid on such loans is allowed as business expense.
- Business insurance
- If you are taking any insurance for business premises like building or insurance for material used in business like stock insurance, this insurance is allowed as business expense
- Even insurance of staff life taken by business is also allowed as business expense.
- Rent Deduction
- If you are running business in rented premises, then rent paid can be claimed as deduction from business income
- Start up cost expense
- If you are starting new business, then expense incurred on research, professional consultancy fees paid for starting business and travelling for business purpose before starting business is allowed as deduction from income in later years.

